GPU gems are back :’o
-
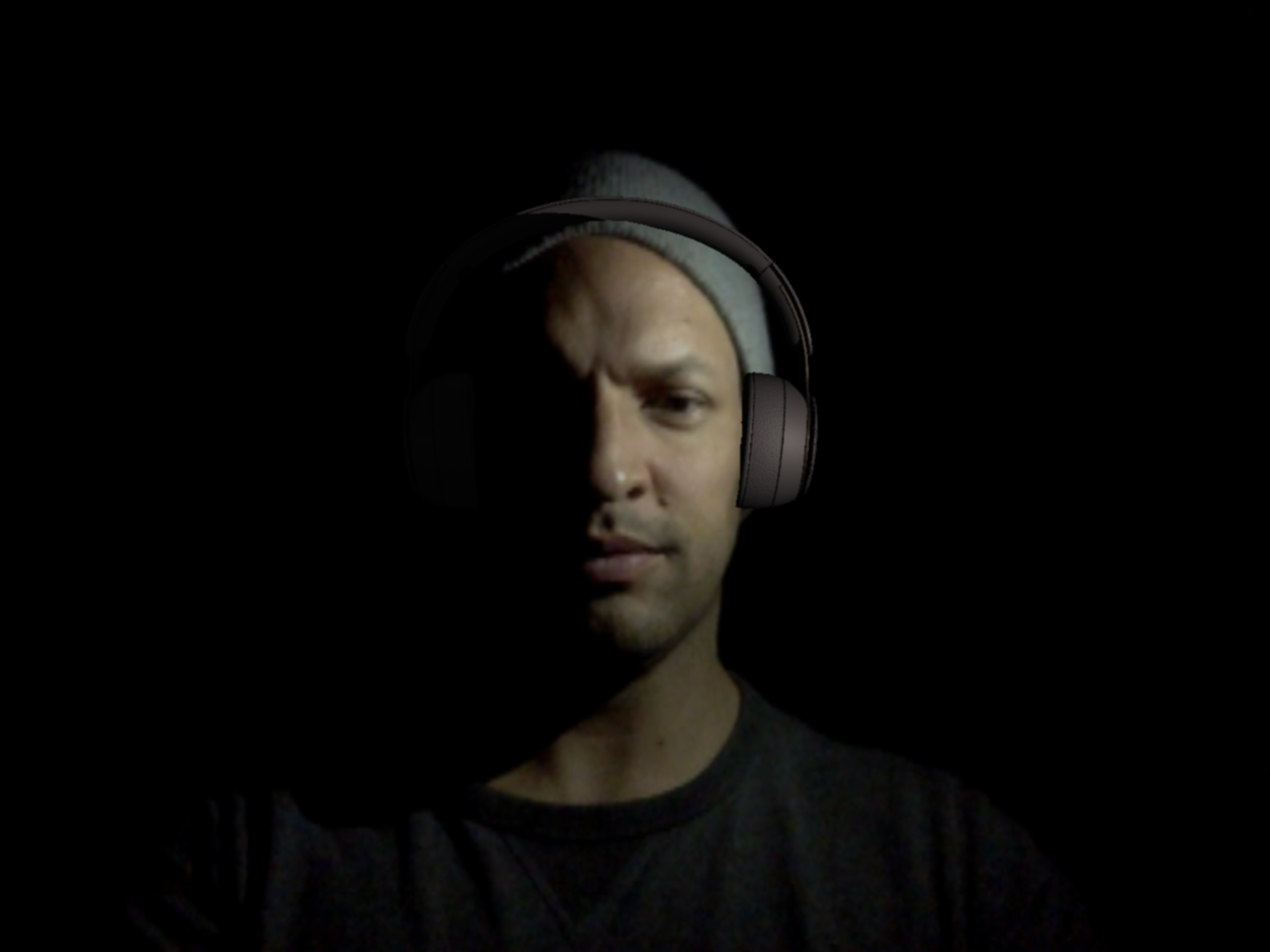

A Naive Approach to Find the Main Light Source for 3d Face Tracking
For one of the latest projects I was working with Drew and Maxime we were working on a virtual try on used to test headphones sets using AR, the app was based on the Beyond Reality Face Tracking library used to make real time face tracking from a video feed. This library provides a complete…
-
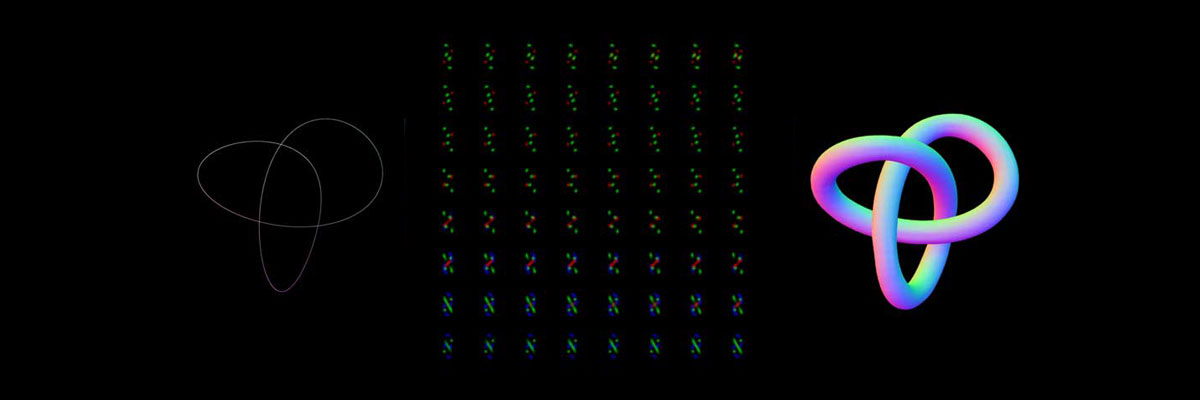
GPU Marching Cubes from Point Clouds in WebGL (part 2: marching cubes steps)
Before reading any further… The author assumes that the reader understands the implementation of the marching cubes algorithm in the CPU, also has knowledge on how to perform a stream compaction over a texture using histopyramids. Please refer to http://paulbourke.net/geometry/polygonise/ and http://www.miaumiau.cat/2016/10/stream-compaction-in-webgl/ for more information about these subjects. Marching Cubes Steps: The marching cubes algorithm…
-

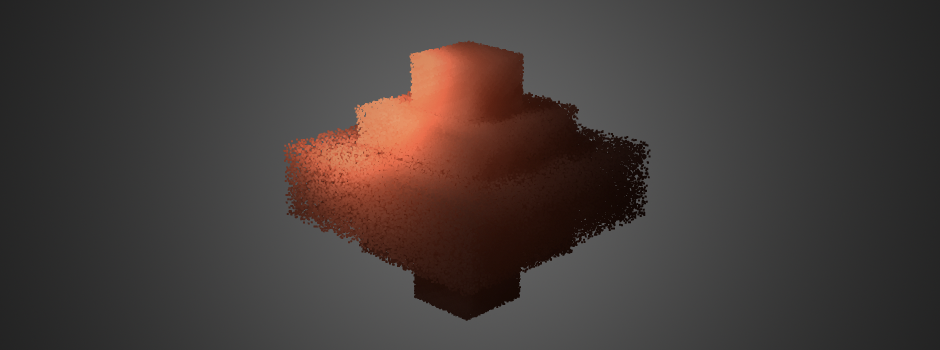
GPU Marching Cubes from Point Clouds in WebGL (part 1: Potential Generation)
In order to render fluids in webGL from particles simulations, an implicit surface method has to be used to create a mesh from a point cloud that represents the current state of the simulation on each frame. To do so there are many algorithms that can be applied, being the Marching Cubes a good approach…
-
Stream Compaction in WebGL
One of the big limitations when doing GPGPU computing is that since the architecture is designed to work on parallel, re arranging or compacting data is a non trivial task on the GPU, to overcome this limitation different stream compaction methods have been created, being histopyramids the algorithm that will be discussed in this post.…
-

Deconstructing Melvin
Deconstructing Melvin: Some time has passed since we have posted anything, so we are going to try to write something somehow interesting. This post is versed about the making of the one sweet project developed in our studio, it is called #translatingmelvin. Project: On December of 2011 we received one call from Ruben Martínez of…
-
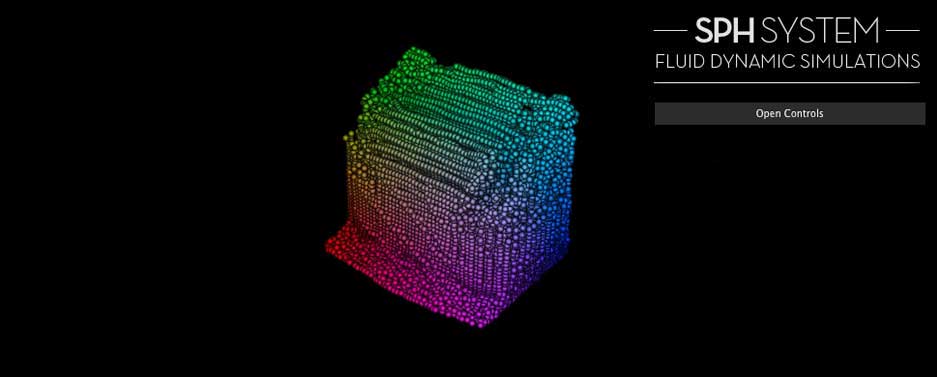
Fluid Simulation with SPH (Smoothed particle hydrodynamics) in WebGL
VIEW THE EXAMPLE The next video is recorded on real time with an AMD Radeon 6970M HD (2Gb), feel free to watch the video if the simulation does not run in your computer. Some links to start When I was reading information about shadows particles for the previous posts, I saw one demo that really called my…
-

Curl Noise + Volume Shadow particles
view the high resolution example view the mid resolution example view the low resolution example A good link is a good gift… When we try to code anything in our studio, the first thing we do is to search for information about the subject in order to find papers and techniques that could help us…
-

Shadow Particles (part II: Optimizations)
VIEW THE EXAMPLE In the last post we talked about the implementation of volume shadows in a particle system, this last approach used a couple of for loops in order to define the final shadow intensity for each particle. This loops could make that the application has to evaluate 32 * nParticles the shadow map,…
-
Shadow Particles (part I: Shadow Mapping)
VIEW EXAMPLE About one year without writing so, this is the first of three very verbose posts about shadow particles… One year and a half ago Félix and me were talking about how we could implement a good shading effect for a particle system made in Flash. In those days people could render 100.000 particles…
-

Surface Tracker
VIEW EXAMPLE Many sites have been done implementing the interaction between video and photos, text, or any other additional assets that could be inserted in the original video to enhance the final experience. Tracking simple planes can be done very easy with the help of After-Effects or any other post- production software, but when it…